7. Architecture Repository
7.1 Overview
Operating a mature Architecture Capability within a large enterprise creates a huge volume of architectural output. Effective management and leverage of these architectural work products require a formal taxonomy for different types of architectural asset alongside dedicated processes and tools for architectural content storage.
This section provides a structural framework for an Architecture Repository that allows an enterprise to distinguish between different types of architectural assets that exist at different levels of abstraction in the organization. This Architecture Repository is one part of the wider Enterprise Repository, which provides the capability to link architectural assets to components of the Detailed Design, Deployment, and Service Management Repositories.
At a high level, the following classes of architectural information are expected to be held within an Architecture Repository:
- The Architecture Metamodel describes the organizationally tailored application of an architecture framework, including a method for architecture development and a metamodel for architecture content
- The Architecture Capability defines the parameters, structures, and processes that support governance of the Architecture Repository
- The Architecture Landscape presents an architectural representation of assets in use, or planned, by the enterprise at particular points in time
- The Standards Library captures the standards with which new architectures must comply, which may include industry standards, selected products and services from suppliers, or shared services already deployed within the organization
- The Reference Library provides guidelines, templates, patterns, and other forms of reference material that can be leveraged in order to accelerate the creation of new architectures for the enterprise
- The Governance Repository provides a record of governance activity across the enterprise
- The Architecture Requirements Repository provides a view of all authorized architecture requirements which have been agreed with the Architecture Board
- The Solutions Landscape presents an architectural representation of the SBBs supporting the Architecture Landscape which have been planned or deployed by the enterprise
The relationships between these areas of the Architecture Repository are shown in Figure 7-1 .
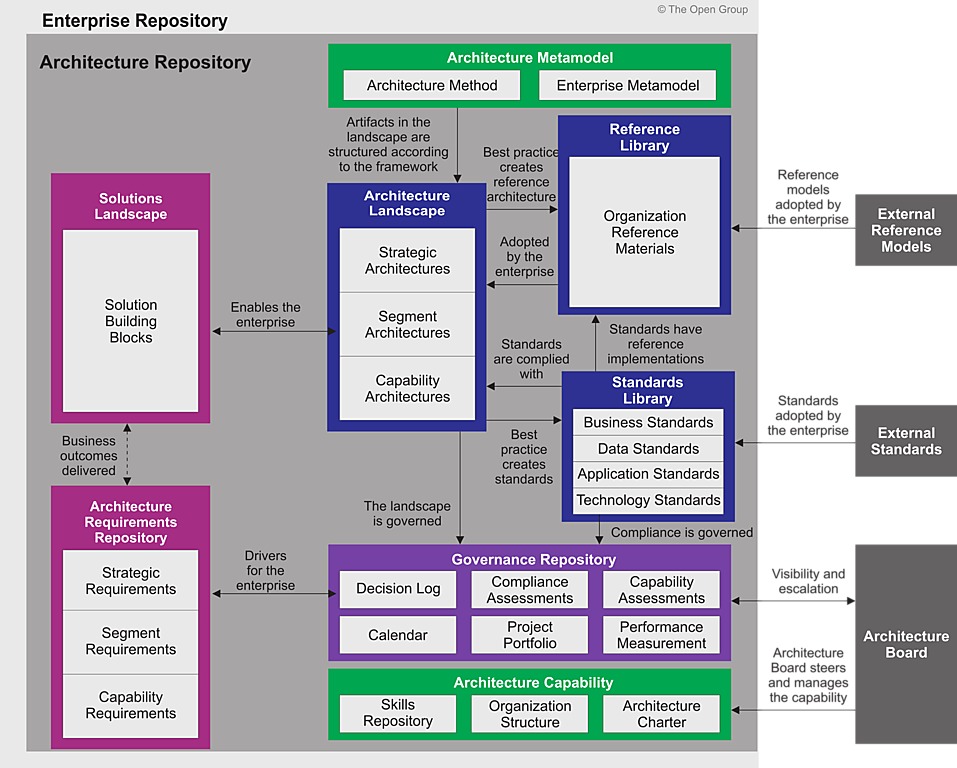
The following sections describe the structure and content of the repository areas.
7.2 Architecture Landscape
The Architecture Landscape holds architectural views of the state of the enterprise at particular points in time. Due to the sheer volume and the diverse stakeholder needs throughout an entire enterprise, the Architecture Landscape is divided into three levels of granularity:
- Strategic Architectures (see the TOGAF Standard — Architecture Development Method) show a long-term summary view of the entire enterprise. Strategic Architectures provide an organizing framework for operational and change activity and allow for direction setting at an executive level.
- Segment Architectures (see the TOGAF Standard — Architecture Development Method) provide more detailed operating models for areas within an enterprise. Segment Architectures can be used at the program or portfolio level to organize and operationally align more detailed change activity.
- Capability Architectures (see the TOGAF Standard — Architecture Development Method) show in a more detailed fashion how the enterprise can support a particular unit of capability. Capability Architectures are used to provide an overview of current capability, target capability, and capability increments and allow for individual work packages and projects to be grouped within managed portfolios and programs.
7.3 Reference Library
7.3.1 Overview
The Reference Library provides a repository to hold reference materials that should be used to develop architectures. Reference materials held may be obtained from a variety of sources, including:
- Standards bodies
- Product and service vendors
- Industry communities or forums
- Standard templates
- Enterprise best practice
The Reference Library should contain:
- Reference Architectures
- Reference Models
- Viewpoint Library
- Templates
- Note:
- The terms reference architecture and reference model are not used carefully in most literature. Reference architecture and reference model have the same relationship as architecture and model. Either can exist as either generic or an organization-specific state. Typically, a generic reference architecture provides the architecture team with an outline of their organization-specific reference architecture that will be customized for a specific organization. For example, a generic reference architecture may identify that there is a need for data models. An example of a reference architecture is the IT4IT Reference Architecture which also defines a common information model for IT management. Another example is the TM Forum eTOM and SID as an organization-specific reference architecture.
In order to segregate different classes of architecture reference materials, the Reference Library can use the Architecture Continuum as a method for classification.
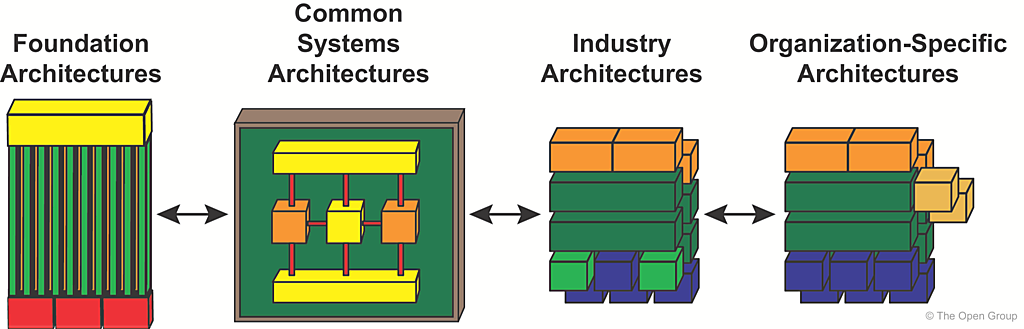
The Architecture Continuum, as shown in Figure 7-2 , can be viewed as a Reference Library classification scheme. As such it illustrates how reference architectures can be organized across a range — from Foundation Architectures, and Industry-Specific Architectures, to an Organization-Specific Architecture.
The enterprise needs and business requirements are addressed in decreasing abstraction from left to right. The architect will typically find more re-usable architectural elements toward the left of the range. When elements are not found, the requirements for the missing elements are passed to the left of the range for incorporation.
Through this exercise it is important to keep in mind the concepts of levels and partitions. At different levels of granularity there may exist reference materials appropriate to the level, and partitions within the Architecture Landscape can be expected to use different reference material (see the TOGAF Standard — Applying the ADM).
7.4 Standards Library
7.4.1 Overview
The Standards Library provides a repository area to hold a set of specifications, to which architectures must conform. Establishment of a Standards Library provides an unambiguous basis for Architecture Governance because:
- The standards are easily accessible to projects and therefore the obligations of the project can be understood and planned for
- Standards are stated in a clear and unambiguous manner, so that compliance can be objectively assessed
7.4.2 Types of Standard
Standards typically fall into three classes:
- Legal and Regulatory Obligations: these standards are mandated by law and therefore an enterprise must comply or face serious consequences
- Industry Standards: these standards are established by industry bodies, such as The Open Group, and are then selected by
the enterprise for adoption
Industry Standards offer potential for interoperation and sharing across enterprises, but also fall outside of the control of the enterprise and therefore must be actively monitored.
- Organizational Standards: these standards are set within the organization and are based on business aspiration (e.g.,
selection of standard applications to support portfolio consolidation)
Organizational Standards require processes to allow for exemptions and standards evolution.
7.4.3 Standards Lifecycle
Standards do not generally exist for all time. New standards are identified and managed through a lifecycle process.
Typically, standards pass through the following stages:
- Proposed Standard: a potential standard has been identified for the organization, but has not yet been evaluated for adoption
- Provisional Standard (also known as a Trial Standard): a Provisional Standard has been identified as a potential
standard for the organization, but has not been tried and tested to a level where its value is fully understood
Projects wishing to adopt Provisional Standards may do so, but under specific pilot conditions, so that the viability of the standard can be examined in more detail.
- Standard (also known as an Active Standard): a Standard defines a mainstream solution that should generally be used as the approach of choice
- Phasing-Out Standard (also known as a Deprecated Standard): a Phasing-Out Standard is approaching the end of its
useful lifecycle
Projects that are re-using existing components can generally continue to make use of Phasing-Out Standards. Deployment of new instances of the Phasing-Out Standard is generally discouraged.
- Retired Standard (also known as an Obsolete Standard): a Retired Standard is no longer accepted as valid within
the landscape
In most cases, remedial action should be taken to remove the Retired Standard from the landscape. Change activity on a Retired Standard should only be accepted as a part of an overall decommissioning plan.
All standards should be periodically reviewed to ensure that they sit within the right stage of the standards lifecycle. As a part of standards lifecycle management, the impact of changing the lifecycle status should be addressed to understand the landscape impact of a standards change and plan for appropriate action to address it.
7.4.4 Standards Classification within the Standards Library
Standards within the Standards Library are categorized according to the building blocks within the TOGAF Enterprise Metamodel. Each metamodel entity can potentially have standards associated with it (e.g., Business Service, Technology Component).
Standards may relate to "approved" building blocks (e.g., a list of standard technology components) or may specify appropriate use of a building block (e.g., scenarios where messaging infrastructure is appropriate, application communication standards are defined).
At the top level, standards are classified in line with the TOGAF architecture domains, including the following areas:
- Business Standards:
- Standard shared business capabilities
- Standard role and actor definitions
- Security and governance standards for business activity
- Data Standards:
- Standard coding and values for data
- Standard structures and formats for data
- Standards for origin and ownership of data
- Restrictions on replication and access
- Applications Standards:
- Standard/shared applications supporting specific business functions
- Standards for application communication and interoperation
- Standards for access, presentation, and style
- Technology Standards;
- Standard hardware products
- Standard software products
- Standards for software development
7.5 Governance Repository
7.5.1 Overview
The Governance Repository provides a repository area to hold shared information relating to the ongoing governance of projects. Maintaining a shared repository of governance information is important, because:
- Decisions made during projects (such as standards deviations or the rationale for a particular architectural approach) are
important to retain and access on an ongoing basis
For example, if a system is to be replaced, having sight of the key architectural decisions that shaped the initial implementation is highly valuable as it will highlight constraints that may otherwise be obscured.
- Many stakeholders are interested in the outcome of project governance (e.g., other projects, customers of the project, the Architecture Board, etc.)
7.5.2 Contents of the Governance Repository
The Governance Repository should contain the following items:
- Decision Log: a log of all architecturally significant decisions that have been made in the organization
This would typically include:
- Product selections
- Justification for major architectural features of projects
- Standards deviations
- Standards lifecycle changes
- Change Request evaluations and approvals
- Re-use assessments
- Compliance Assessments: at key checkpoint milestones in the progress of a project, a formal architecture review will be
carried out
This review will measure the compliance of the project to the defined architecture standards. For each project, this log should include:
- Project overview
- Progress overview (timeline, status, issues, risks, dependencies, etc.)
- Completed architecture checklists
- Standards compliance assessment
- Recommended actions
- Capability Assessments: depending on their objectives, some projects will carry out assessments of business, IT, or
Architecture Capability
These assessments should be periodically carried out and tracked to ensure that appropriate progress is being made. This log should include:
- Templates and reference models for executing Capability Assessments
- Business Capability Assessments
- IT capability, maturity, and impact assessments
- Architecture maturity assessments
- Calendar: the Calendar should show a schedule of in-flight projects and formal review sessions to be held against these projects
- Project Portfolio: the Project Portfolio should hold summary information about all in-flight projects that fall under
Architecture Governance, including:
- The name and description of the project
- Architectural scope of the project
- Architectural roles and responsibilities associated with the project
- Performance Measurement: based on a charter for the architecture function, a number of performance criteria will
typically be defined
The Performance Measurement log should capture metrics relating to project governance and any other performance metrics relating to the architecture charter so that performance can be measured and evaluated on an ongoing basis.
7.6 The Architecture Requirements Repository
7.6.1 Overview
The Architecture Requirements Repository is used by all phases of the ADM to record and manage all information relevant to the architecture requirements. The requirements address the many types of architecture requirements; i.e., strategic, segment, and capability requirements which are the major drivers for the Enterprise Architecture.
Requirements can be gathered at every stage of the architecture development cycle and need to be approved through the various phases and governance processes.
The Requirements Management phase is responsible for the management of the contents of the Architecture Requirements Repository and ensuring the integrity of all requirements and their availability for access by all phases.
7.6.2 Contents of the Architecture Requirements Repository
The Architecture Requirements Repository holds architectural requirements of the required state of the enterprise at particular points in time. Due to the sheer volume and the diverse stakeholder needs throughout the architecture development cycle, the Architecture Requirements are divided into three levels of granularity:
- Strategic Architecture Requirements show a long-term summary view of the requirements for the entire enterprise.
Strategic Architecture Requirements identify operational and change requirements for direction setting at an executive level.
- Segment Architecture Requirements provide more detailed operating model requirements for areas within an enterprise.
Segment Architecture Requirements may identify requirements at the program or portfolio level to identify and align more detailed change activity.
- Capability Architecture Requirements identify the detailed requirements for a particular unit of capability.
Capability Architecture Requirements identify requirements for individual work packages and projects to be grouped within managed portfolios and programs.
The business outcomes for architecture requirements will be reflected in the Solutions Landscape over time. When this occurs, the architecture requirements are met and archived for audit purposes.
7.7 Solutions Landscape
The Solutions Landscape holds the SBBs which support the ABBS specified, developed, and deployed. The building blocks may be products or services which may be categorized according to the Enterprise Continuum categorization and/or the ABB specifications as Strategic, Segment, or Capability SBBs.
SBBs may also include tools, systems, services, and information which describe the actual solutions that may be selected and their operation. For example, vendor-specific reference models or vendor-specific Levels 4 and 5 of the IT4IT Reference Architecture would be defined here.
However, the Solutions Landscape will not include the information and data content produced by the solutions selected; that is the responsibility of the solutions themselves.
7.8 The Enterprise Repository
While the Architecture Repository holds information concerning the Enterprise Architecture and associated specifications and artifacts, there are a considerable number of enterprise repositories that support the architecture both inside and outside of the enterprise.
These can include development repositories, specific operating environments, instructions, and configuration management
repositories.
7.9 External Repositories
7.9.1 External Reference Models
There are many industry reference models available which may assist in understanding the role of and developing the reference architectures.
7.9.2 External Standards
These relate to industry, best practice, or formal defined standards used by leading organizations. Examples include ISO, IEEE, and Government standards.
7.9.3 Architecture Board Approvals
Decisions made by the Architecture Board which affect the Enterprise Architecture are often recorded in the minutes of meetings. These minutes are often held in documentation archives which are excluded from the Architecture Repository for legal or regulatory reasons.
TOGAF is a registered trademark of The Open Group
 return to top of page
return to top of page